Image Classification
정의
이미지를 입력 받았을 때
이미지의 클래스를 예측하는 모델
Cat(0.95), Dog(0.05) 와 같이 확률로 나타나며
그 중 확률이 가장 높은 클래스가 해당한다

CNN(Convolutional Neural Network)
Image classification 중 가장 많이 쓰이는 딥러닝 모델 중 하나
이미지 처리에 특화되어 있다
Convolution이라는 패치를 통해
weight를 갱신하고 연산하며, pooling, fully connected layer 등의 연산 방법을 사용할 수 있다

History of Image Classification
대표적인 CNN의 역사

다양한 Image classification을 위한 Datasets
ImageNet, CIFAR-10, CIFAR-100, MNIST 등 다양한 데이터셋이 존재하며,
Paperwithcodes 사이트와 같은 곳에서 모델과 함께 확인할 수 있다
예제
가상환경 설정
Ubuntu의 경우 docker 환경, windows 등의 경우 anaconda를 통해 가상환경을 구성한다
가상 환경 설정에 대한 정보는 다른 사이트를 참고한다
Mac에서 진행한다
conda를 설치한 후 가상 공간을
아래 명령어와 같이 설정한다
conda create -n pytorch_py38 python=3.8진행한다

activate pytorch_py38
명령어를 통해 가상 환경을 활성화한 후
가상 환경 내에 pytorch를 설치한다
Mac에서 conda를 사용하는 경우 아래 명령어를 입력한다
conda install pytorch::pytorch torchvision torchaudio -c pytorchPytorch
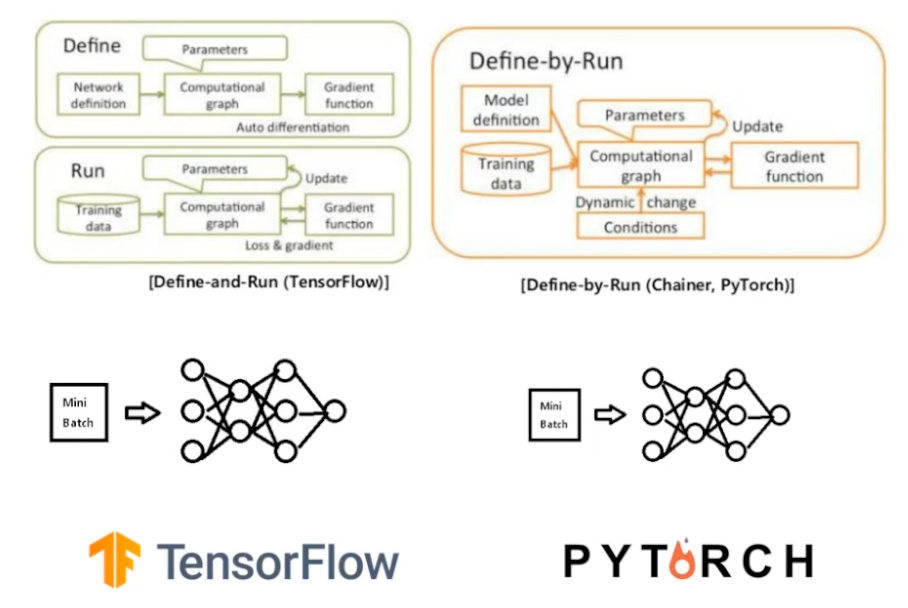
why Pytorch?
Define by Run 구조로 모델을 완전히 설계하지 않아도 중간에 결과를 뽑을 수 있기 때문에
코드를 직관적으로 짤 수 있다
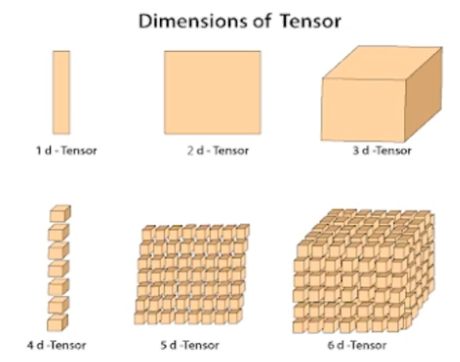
Tensor
1D~ND 차원까지 다양한 차원으로 정의되는 데이터 타입이다
CNN에서 연산하기 적합한 데이터 타입이다
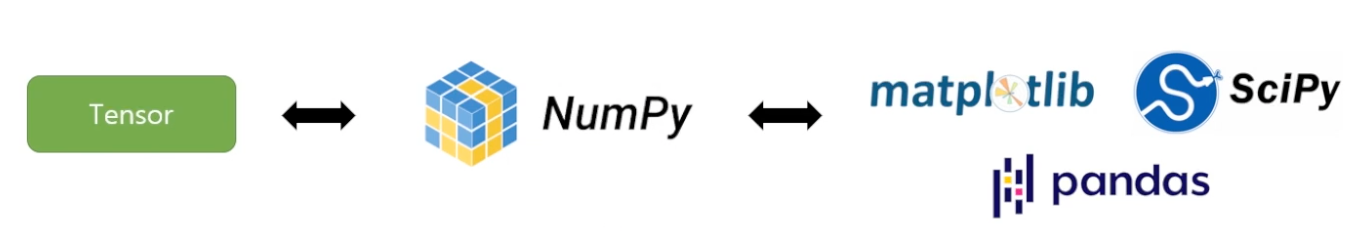
입력 데이터가 들어오면
tensor로 변환한 후
weight 과 곱해졌을 때 나타나는 결과도 tensor와 같이 나타난다

또한 numpy로 데이터 변환이 가능하고
이를 통해 다양한 라이브러리를 사용하여
시각화, 분석 등 다양한 방법으로 접근할 수 있다
Code
import torch
import numpy as np
# test torch
"""
x = torch.rand(5,3)
print(x)"""
def make_tensor():
# int16
a = torch.tensor([[1,2],[3,4]], dtype = torch.int16)
# float
b = torch.tensor([2], dtype = torch.float32)
# double
c = torch.tensor([3], dtype=torch.float64)
print(a,b,c)
tensor_list = [a,b,c]
for t in tensor_list:
print("shape of tensor {}".format(t.shape))
print("datatpye of tensor {}".format(t.dtype))
# data가 저장된 장치 확인
print("device tensor is sorted on {}".format(t.device))
def sumsub_tensor():
a = torch.tensor([3,2])
b = torch.tensor([5,3])
print("input: {}. {}".format(a, b))
# sum
sum = a + b
print("sum: {}".format(sum))
# sub
sub = a - b
print("sub: {}".format(sub))
# sum each element
sum_element_a = a.sum()
print(sum_element_a)
def muldiv_tensor():
# initialize 0 to 8 and change size to 3 by 3
a = torch.arange(0,9).view(3,3)
b = torch.arange(0,9).view(3,3)
print("two input tensors are \n{}, \n and {}".format(a,b))
# mat mul
c = torch.matmul(a,b)
print(c)
# elementalwise mul
d = torch.mul(a,b)
print(d)
def reshape_tensor():
a = torch.tensor([2,4,5,6,7,8])
print("input tensor: \n{}".format(a))
# view
b = a.view(2,3)
print("view \n{}".format(b))
# transpose
bt = b.t()
print("transpose \n {}".format(bt))
def access_tensor():
a = torch.arange(1,13).view(4,3)
print("input: \n{}".format(a))
# first row(slicing)
print(a[:,0])
# first col
print(a[0,:])
# [1,1]
print(a[1,1])
def transform_numpy():
a = torch.arange(1,13).view(4,3)
print("input: \n{}".format(a))
a_np = a.numpy()
print("numpy: {}".format(a_np))
b = np.array([1,2,3])
b_t = torch.from_numpy(b)
print(b)
# assemble in parallel and keep the shape
def concat_tensor():
a = torch.arange(1,10).view(3,3)
b = torch.arange(10, 19).view(3,3)
c = torch.arange(20,29).view(3,3)
# set the dim to concat
abc = torch.cat([a,b,c],dim=0)
print("input tensor: \n{} \n{} \n{}".format(a,b,c))
print("concat: \n{}".format(abc))
# add the dimension
def stack_tensor():
a = torch.arange(1,10).view(3,3)
b = torch.arange(10, 19).view(3,3)
c = torch.arange(20,29).view(3,3)
# set the dim to stack
abc = torch.stack([a,b,c],dim=1)
print("input tensor: \n{} \n{} \n{}".format(a,b,c))
print("stack: \n{}".format(abc))
def transpose_tensor():
a = torch.arange(1,10).view(3,3)
# transpose selected dimension
at = torch.transpose(a,0,1)
print("input: \n{}".format(a))
print("transpose: \n{}".format(at))
b = torch.arange(1,25).view(4,3,2)
print("input b tensor: \n{}".format(b))
bt = torch.transpose(b,0,2)
print("transpose: \n{}".format(bt))
print(bt.shape)
bp = b.permute(2,0,1) # 0,1,2
print("permute: \n{}".format(bp))
print(bp.shape)
if __name__ == "__main__":
#make_tensor()
#sumsub_tensor()
#muldiv_tensor()
#reshape_tensor()
#access_tensor()
#transform_numpy()
#concat_tensor()
#stack_tensor()
transpose_tensor()Assignment

'AI > ML' 카테고리의 다른 글
| [ML] 혼자 공부하는 머신러닝+딥러닝 Ch.6 (0) | 2023.08.29 |
|---|---|
| [ML] 혼자 공부하는 머신러닝+딥러닝 Ch.5 (0) | 2023.08.21 |
| [ML] 혼자 공부하는 머신러닝+딥러닝 Ch.4 (0) | 2023.08.15 |
| [ML] 혼자 공부하는 머신러닝+딥러닝 Ch.3 (0) | 2023.08.08 |
| [ML] 혼자 공부하는 머신러닝+딥러닝 Ch.1 & 2 (0) | 2023.08.01 |